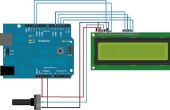
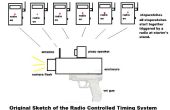
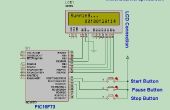
Paso 4: código
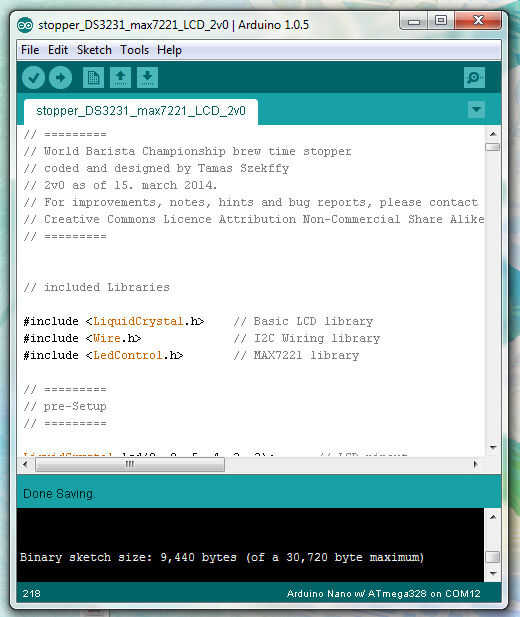
El código siguiente debe ser copiado y pegado en el IDE de Arduino y luego, si se hizo algunos cambios necesarios, debe cargarse en la placa Arduino.
Descarga directa como .ide archivo, haga clic en este enlace.
// ========== // World Barisa Championship brew time stopper // coded and designed by Tamas Szekffy // 2v0 as of 15. march 2014. // For improvements, notes, hints and bug reports, please contact professzore // Creative Commons Licence Attribution Non-Commercial Share Alike (CC-BY-NC-SA-4.0) // ========== // included Libraries #include // Basic LCD library #include // I2C Wiring library #include // MAX7221 library // ========== // pre-Setup // ========== LiquidCrystal lcd(8, 9, 5, 4, 3, 2); // LCD pinout const byte dot = B10100101; const byte full = B11111111; const int LCDBK = 6; // LCD Backlight pin const int ss1 = A3; // Start/Stop 1 pin const int ss2 = A2; // Start/Stop 2 pin const int rst = A1; // Reset pin int bcklght = 200; // LCD Backlight value (0 = turn off backlight) // Timer variables boolean timer1 = false; // true, if timer1 is running boolean timer2 = false; // true, if timer2 is running boolean ssastate = false; // became true, if ss1 button pressed (used for debouncing) boolean ssbstate = false; // became true, if ss2 button pressed (used for debouncing) boolean rststate = false; // became true, if rst button pressed (used for debouncing) boolean finish = false; // became true, as soon as all measurements finished unsigned long atime; // temporary variable for first time, indicates the time spent since start unsigned long btime; // temporary variable for second time, indicates the time spent since start unsigned long astime; // variable for first time, indicates the time when stopper started unsigned long bstime; // variable for second time, indicates the time when stopper started unsigned long debounce; int atimes[3]; // arrays of variables to store first time measured, one after another int btimes[3]; // arrays of variables to store second time measured, one after another int validtime = 3000; // maximum time allowed as difference between measured times to meet WBC rules (milliseconds, 3 sec = 3000) unsigned long menudelay = 0; // variable to measure the time how long "reset" pressed boolean menustate = false; // boolean variable to point out if the system is in MENU mode for validation time boolean menustate2 = false; // boolean variable to point out if the system is in MENU mode for backlight setting time byte atimecount = 0; // variable to count which measurement (first, second or first) are 'in line' for first time byte btimecount = 0; // variable to count which measurement (first, second or first) are 'in line' for second time /* pin 11 is connected to the DataIn pin 13 is connected to the CLK pin 10 is connected to LOAD We have only a single (1) MAX72XX. */ LedControl lc=LedControl(11,13,10,1); // =========== // Main Setup // =========== void setup() { Wire.begin(); // Turn on I2C analogWrite(LCDBK, bcklght); // LCD backlight is ON lcd.begin(16, 2); // set the size of the LCD (16 digits, 2 rows) lcd.clear(); /* The MAX72XX is in power-saving mode on startup, we have to do a wakeup call */ lc.shutdown(0,false); /* Set the brightness */ lc.setIntensity(0,8); /* and clear the display */ lc.clearDisplay(0); pinMode(ss1, INPUT); pinMode(ss2, INPUT); pinMode(rst, INPUT); // testrun(); // unmark '//' if you need the initial test of the system // delay(1); lcd.clear(); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print("WBC valid time"); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print(validtime); lcd.print(" msec"); delay(2000); lcd.clear(); rstall(); } // ============= // Main routine // ============= void loop() { if (digitalRead(ss1) == HIGH && ssastate == false && finish != true && debounce + 200 < millis()) { startstopa(); debounce = millis(); } if (digitalRead(ss1) == LOW && ssastate == true) { ssastate = false; } if (digitalRead(ss2) == HIGH && ssbstate == false && finish != true && debounce + 200 < millis()) { startstopb(); debounce = millis(); } if (digitalRead(ss2) == LOW && ssbstate == true) { ssbstate = false; } if (digitalRead(rst) == HIGH && rststate == false && finish == true && debounce + 200 < millis()) { rstall(); debounce = millis(); finish = false; menudelay = 0; } if (digitalRead(rst) == HIGH && rststate == false && finish == false && menudelay == 0) { menudelay = millis() + 3000; rststate = true; } if (digitalRead(rst) == HIGH && rststate == true && menudelay != 0 && menudelay < millis()) { menustate = true; lcd.clear(); } if (digitalRead(rst) == LOW && rststate == true) { rststate = false; menudelay = 0; } if (atimecount == btimecount && atimecount != 0) { validate(); } if (atimecount == 3 && btimecount == 3) { finish = true; } // ============================ // Time check value setup/menu // ============================ while(menustate) { lc.clearDisplay(0); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print("WBC valid time"); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print(validtime); lcd.print(" msec "); if (digitalRead(ss1) == HIGH && ssastate == false && validtime > 0 && debounce + 200 < millis()) { ssastate = true; validtime -= 100; debounce = millis(); } if (digitalRead(ss1) == LOW && ssastate == true) { ssastate = false; } if (digitalRead(ss2) == HIGH && ssbstate == false && validtime < 32700 && debounce + 200 < millis()) { ssbstate = true; validtime += 100; debounce = millis(); } if (digitalRead(ss2) == LOW && ssbstate == true) { ssbstate = false; } if (digitalRead(rst) == LOW && rststate == true) { rststate = false; menudelay = 0; } if (digitalRead(rst) == HIGH && rststate == false && menudelay == 0) { menustate = false; menustate2 = true; rststate = true; menudelay = millis() + 200; } } // END of submenu1 // ===================== // Backlight setup menu // ===================== while(menustate2) { lc.clearDisplay(0); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print("Backlight value"); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print(bcklght); lcd.print(" "); if (digitalRead(ss1) == HIGH && ssastate == false && bcklght > 0 && debounce + 200 < millis()) { ssastate = true; bcklght -= 10; debounce = millis(); } if (digitalRead(ss1) == LOW && ssastate == true) { ssastate = false; } if (digitalRead(ss2) == HIGH && ssbstate == false && bcklght < 250 && debounce + 200 < millis()) { ssbstate = true; bcklght += 10; debounce = millis(); } if (digitalRead(ss2) == LOW && ssbstate == true) { ssbstate = false; } if (digitalRead(rst) == LOW && rststate == true) { rststate = false; menudelay = 0; } if (digitalRead(rst) == HIGH && rststate == false && menudelay > millis()) { menustate2 = false; rststate = true; delay(1); rstall(); delay(1); } analogWrite(LCDBK, bcklght); } // END of submenu2 delay(1); } // ======================== // Start/stop of stopper 1 // ======================== void startstopa() { ssastate = true; // the button has pressed if (timer1 == false) // if the timer is NOT running... { astime = millis(); // record start time timer1 = true; // indicate the start of the timer lcd.setCursor(2,0); lcd.print("RUN"); lc.setChar(0,3,'-',false); } else // if the timer is running... { timer1 = false; // indicate the stop of the timer atime = millis() - astime; // calculates the time spent since start lcd.setCursor(2,0); lcd.print("..."); lc.setChar(0,3,' ',false); atime = atime/100; atime = atime * 100; atimes[atimecount] = atime; write7Segment(atimes[atimecount], 0); if (atimecount < 3) { lcd.setCursor(6+(atimecount*2),0); lcd.write(full); atimecount ++; } } } // ======================== // Start/stop of stopper 2 // ======================== void startstopb() { ssbstate = true; // the button has pressed if (timer2 == false) // if the timer is NOT running... { bstime = millis(); // record start time timer2 = true; // indicate the start of the timer lcd.setCursor(2,1); lcd.print("RUN"); lc.setChar(0,7,'-',false); } else // if the timer is running... { timer2 = false; // indicate the stop of the timer btime = millis() - bstime; // calculates the time spent since start lcd.setCursor(2,1); lcd.print("..."); lc.setChar(0,7,' ',false); btime = btime/100; btime = btime * 100; btimes[btimecount] = btime; write7Segment(btimes[btimecount], 4); if (btimecount < 3) { lcd.setCursor(6+(btimecount*2),1); lcd.write(full); btimecount ++; } } } // =================== // Write time on 7221 // =================== void write7Segment(unsigned long v, byte i) { byte ones; byte tens; byte fractions; v = v/100; fractions = v%10; v = v/10; ones = v%10; v = v/10; tens = v%10; lc.setDigit(0,i,tens,false); lc.setDigit(0,i+1,ones,true); lc.setDigit(0,i+2,fractions,false); } // ================================ // Validate each measurement-pairs // ================================ void validate() { unsigned int lowest; unsigned int highest; unsigned int difference; lowest = min(atimes[atimecount-1],btimes[btimecount-1]); highest = max(atimes[atimecount-1],btimes[btimecount-1]); difference = highest - lowest; if (difference > validtime) { lcd.setCursor(12,0); lcd.print("FAIL"); byte ones; byte tens; byte fractions; difference = difference/100; fractions = difference%10; difference = difference/10; ones = difference%10; difference = difference/10; tens = difference%10; lcd.setCursor(12,1); lcd.print(tens); lcd.setCursor(13,1); lcd.print(ones); lcd.setCursor(14,1); lcd.print('.'); lcd.setCursor(15,1); lcd.print(fractions); } else { lcd.setCursor(12,0); lcd.print(" OK "); byte ones; byte tens; byte fractions; difference = difference/100; fractions = difference%10; difference = difference/10; ones = difference%10; difference = difference/10; tens = difference%10; lcd.setCursor(12,1); lcd.print(tens); lcd.setCursor(13,1); lcd.print(ones); lcd.setCursor(14,1); lcd.print('.'); lcd.setCursor(15,1); lcd.print(fractions); } } // =========================================== // Reset all values, returns to initial state // =========================================== void rstall() { rststate = true; lc.clearDisplay(0); delay(100); write7Segment(0, 0); write7Segment(0, 4); //reset all variables timer1 = false; timer2 = false; atime = 0; btime = 0; astime = 0; bstime = 0; atimes[0] = 0; atimes[1] = 0; atimes[2] = 0; btimes[0] = 0; btimes[1] = 0; btimes[2] = 0; atimecount = 0; btimecount = 0; lcd.clear(); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print('1'); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print('2'); lcd.setCursor(2,0); lcd.print("..."); lcd.setCursor(2,1); lcd.print("..."); lcd.setCursor(6,0); lcd.write(dot); lcd.setCursor(8,0); lcd.write(dot); lcd.setCursor(10,0); lcd.write(dot); lcd.setCursor(6,1); lcd.write(dot); lcd.setCursor(8,1); lcd.write(dot); lcd.setCursor(10,1); lcd.write(dot); lcd.setCursor(12,0); lcd.print("...."); lcd.setCursor(12,1); lcd.print("...."); } // ======================================================================== // Test routine, may be started by un-// the call at the end of void.Setup // ======================================================================== void testrun() { lc.clearDisplay(0); lcd.clear(); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print("WBC Stopwatch"); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print("Made by Tamas Szekffy in 2014"); delay(2000); for (int scroll = 0; scroll < 18; scroll++) { lcd.scrollDisplayLeft(); delay(500); } lcd.clear(); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print("Test run will"); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print("undergo in 5 s"); delay(5000); lcd.clear(); lc.clearDisplay(0); for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { lc.setDigit(0,0,i,false); lc.setDigit(0,1,i,true); lc.setDigit(0,2,i,false); lc.setDigit(0,4,i,false); lc.setDigit(0,5,i,true); lc.setDigit(0,6,i,false); delay(500); } lc.clearDisplay(0); delay(500); lcd.clear(); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print('1'); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(0,1); lcd.print('2'); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(2,0); lcd.print("..."); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(2,0); lcd.print("RUN"); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(2,1); lcd.print("..."); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(2,1); lcd.print("RUN"); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(6,0); lcd.write(dot); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(6,0); lcd.write(full); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(8,0); lcd.write(dot); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(8,0); lcd.write(full); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(10,0); lcd.write(dot); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(10,0); lcd.write(full); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(6,1); lcd.write(dot); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(6,1); lcd.write(full); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(8,1); lcd.write(dot); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(8,1); lcd.write(full); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(10,1); lcd.write(dot); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(10,1); lcd.write(full); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(12,0); lcd.print("...."); delay(250); lcd.setCursor(12,1); lcd.print("...."); delay(1000); lcd.clear(); lcd.setCursor(0,0); lcd.print("Ready to GO!"); delay(3000); lcd.clear();}